Specifying connection properities v55
Migration Toolkit uses the configuration and connection information stored in the toolkit.properties file during the migration process to identify and connect to the source and target databases.
On Linux, the toolkit.properties file is located in /usr/edb/migrationtoolkit/etc.
On Windows, the file is located in C:\Program Files\edb\mtk\etc.
On Mac OS, the file is located in /Library/edb/mtk/etc.
The figure shows a sample toolkit.properties file:
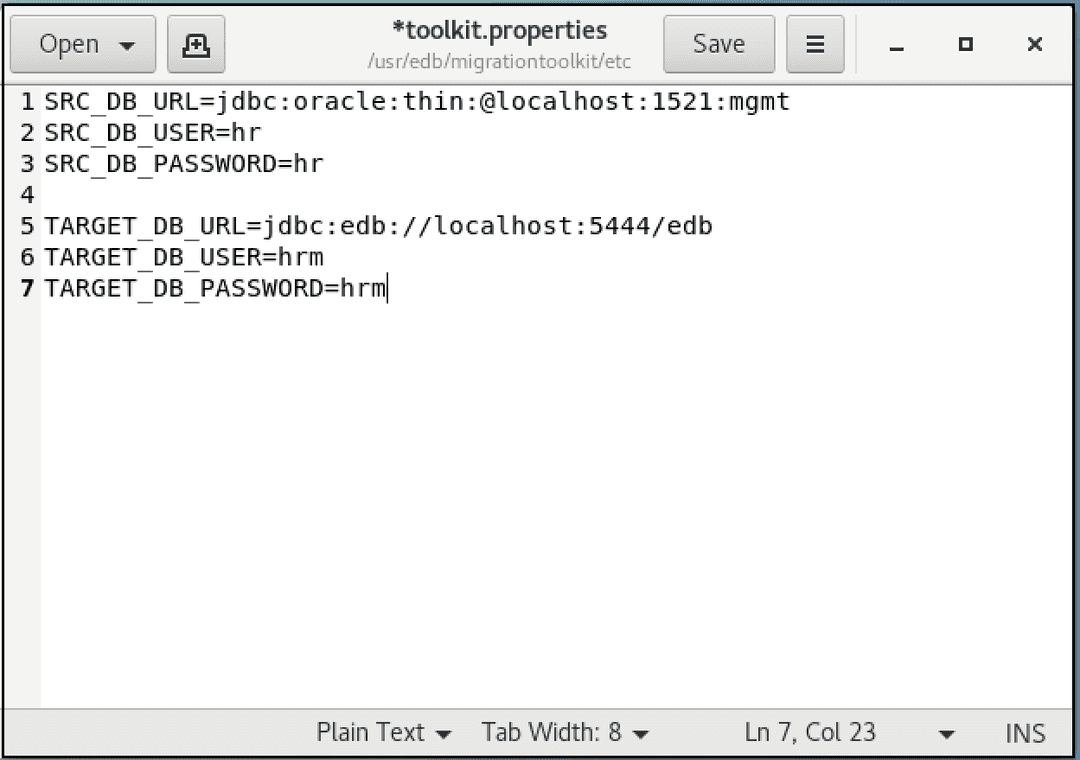
Before executing Migration Toolkit commands, modify the toolkit.properties file with the editor of your choice. Update the file to include the following information:
SRC_DB_URLspecifies how Migration Toolkit connects to the source database. Details on forming the URL for each source database follows.SRC_DB_USERspecifies a user name (with sufficient privileges) in the source database.SRC_DB_PASSWORDspecifies the password of the source database user. Provide the password without any surrounding quotes.TARGET_DB_URLspecifies the JDBC URL of the target database.TARGET_DB_USERspecifies the name of a privileged target database user.TARGET_DB_PASSWORDspecifies the password of the target database user. Provide the password without any surrounding quotes.
Note
Unless specified in the command line, Migration Toolkit expects the source database to be Oracle and the target database to be EDB Postgres Advanced Server. For any other source or target database, specify the -sourcedbtype or -targetdbtype options as described in Migrating from a non-Oracle source database.
For specifying a target database on Cloud Service, see Defining the URL and configuring the required parameters for Cloud Service.
URL and parameters for an Advanced Server
Migration Toolkit helps with migration from the following platforms to Advanced Server:
- Oracle
- PostgreSQL
- MySQL
- Sybase
- SQL Server
For a definitive list of the objects migrated from each database type, refer to Functionality overview.
Migration Toolkit reads connection specifications for the source and the target database from the toolkit.properties file. Connection information for each must include:
- The URL of the database
- The name of a privileged user
- The password associated with the specified user
The URL conforms to JDBC standards and takes the form:
{TARGET_DB_URL|SRC_DB_URL}=jdbc:edb://<host>:<port><database_id>An Advanced Server URL contains the following information:
jdbc— The protocol is alwaysjdbc.edb— If you're using Advanced Server, specifyedbfor the subprotocol value.<host>— The name or IP address of the host where the Postgres instance is running.<port>— The port number that the Advanced Server database listener is monitoring. The default port number is 5444.<database_id>— The name of the source or target database.
Ensure these values are set in the toolkit.properties file:
{TARGET_DB_USER|SRC_DB_USER}— Specifies a user with privileges to create each type of object migrated. If migrating data into a table, the specified user might also require insert, truncate, and references privileges for each target table.{TARGET_DB_PASSWORD|SRC_DB_PASSWORD}— Set to the password of the privileged Advanced Server user. Provide the password without any surrounding quotes.
URL and parameters for PostgreSQL
Migration Toolkit helps with migration from the following platforms to PostgreSQL:
- Oracle
- Advanced Server
- MySQL
- SQL Server
For a definitive list of the objects migrated from each database type, refer to Functionality overview.
Migration Toolkit reads connection specifications for the source and the target database from the toolkit.properties file. Connection information for each must include:
- The URL of the database
- The name of a privileged user
- The password associated with the specified user
A PostgreSQL URL conforms to JDBC standards and takes the form:
{SRC_DB_URL|TARGET_DB_URL}=jdbc:postgresql://<host>:<port>/<database_id>The URL contains the following information:
jdbc— The protocol is alwaysjdbc.postgresql— If you're using PostgreSQL, specifypostgresqlfor the subprotocol value.<host>— The name or IP address of the host where the Postgres instance is running.<port>— The port number that the Postgres database listener is monitoring. The default port number is 5432.<database_id>— The name of the source or target database.
Ensure these values are set in the toolkit.properties file:
{SRC_DB_USER|TARGET_DB_USER}— Specify a user with privileges to create each type of object migrated. If migrating data into a table, the specified user might also need insert, truncate, and references privileges for each target table.{SRC_DB_PASSWORD|TARGET_DB_PASSWORD}— Set to the password of the privileged PostgreSQL user. Provide the password without any surrounding quotes.
URL and parameters for Cloud Service
Migration Toolkit helps with migration from the following platforms to Cloud Service:
- Oracle
- Advanced Server
- PostgreSQL
- MySQL
- SQL Server
Migration Toolkit reads connection specifications for the source and the target database from the toolkit.properties file. Connection information for each must include:
- The URL of the database
- The name of a privileged user
- The password associated with the specified user
When migrating to Cloud Service, TARGET_DB_URL takes the form of a JDBC URL. For example:
jdbc:<postgres_type>://<host_name>[:<port>]/<database_id>?sslmode=<sslmode>
Note
Many of the values you need for the target database URL are available from the Cloud Service portal. In Cloud Service, select your cluster and go to the Connect tab to find the values.
The URL contains the following information:
jdbc— The protocol is alwaysjdbc.postgres_type— The subprotocol is the Postgres type. Specifyedbif you're using Advanced Server orpostgresqlif you're using PostgreSQL.<host_name>— The host name of your cluster. You can copy it from the Host field on the Connect tab in the Cloud Service portal.<port>— The port number that the database listener is monitoring. You can copy it from the Port field on the Connect tab in the Cloud Service portal.<database_id>— The name of the target database. Set this to the name of the database in your cluster that you want to use as your migration target database. The name of the default database for your cluster is shown in the Dbname field on the Connect tab in the Cloud Service portal. Often a separate database is created for use as the migration target.sslmode— Either "require" or "verify-full". See Recommended settings for SSL mode. Listed at the end of the Service URI value on the Connect tab in the Cloud Service portal.
Ensure these values are set in the toolkit.properties file:
TARGET_DB_USER— Specifies the name of a privileged database user. You can copy it from the User field on the Connect tab in the Cloud Service portal.TARGET_DB_PASSWORD— Contains the password of the specified user. Provide the password without any surrounding quotes.
URL and parameters for Oracle
Migration Toolkit helps with migration from an Oracle database to a PostgreSQL or Advanced Server database. When migrating from Oracle, you must specify connection specifications for the Oracle source database in the toolkit.properties file. The connection information must include:
- The URL of the Oracle database
- The name of a privileged user
- The password associated with the specified user
When migrating from an Oracle database, SRC_DB_URL must contain a JDBC URL, specified in one of two forms. The first form is:
jdbc:oracle:thin:@<host_name>:<port>:<database_id>
The second form is:
jdbc:oracle:thin:@//<host_name>:<port>{<database_id|service_name>}An Oracle URL contains the following information:
jdbc— The protocol is alwaysjdbc.oracle— The subprotocol is alwaysoracle.thin— The driver type. Specify a driver type ofthin.<host_name>— The name or IP address of the host where the Oracle server is running.<port>— The port number that the Oracle database listener is monitoring.<database_id>— The database SID of the Oracle database.<service_name>— The name of the Oracle service.
Ensure these values are set in the toolkit.properties file:
SRC_DB_USER— Specifies the name of a privileged Oracle user. The Oracle user needs read access to the source database objects you want to migrate. If you want to migrate users/roles and related profiles/privileges, grant the Oracle user SELECT privileges on the following Oracle catalog objects:DBA_ROLESDBA_USERSDBA_TAB_PRIVSDBA_PROFILESDBA_ROLE_PRIVSROLE_ROLE_PRIVSDBA_SYS_PRIVS
SRC_DB_PASSWORD— Contains the password of the specified user. Provide the password without any surrounding quotes.
URL and parameters for an SQL Server
Migration Toolkit helps with migration from an SQL Server database to a PostgreSQL or Advanced Server database. Migration Toolkit supports migration of the following object definitions:
- Schemas
- Tables
- Table data
- Constraints
- Indexes
Migration Toolkit reads connection specifications for the source database from the toolkit.properties file. The connection information must include:
- The URL of the source database
- The name of a privileged user
- The password associated with the specified user
If you're connecting to a SQL Server database, SRC_DB_URL takes the form of a Microsoft JDBC URL (recommended) or a JTDS URL.
Microsoft JDBC URL
By default, Microsoft JDBC Driver for SQL Server uses TLS encryption for all communication between the client and the SQL Server. Set encrypt to false, if you want to disable TLS encryption. For more information about connecting to a Microsoft SQL Server using JDBC type 4 driver, see Building the connection URL.
jdbc:sqlserver://<server_name>:<port>[;databaseName=<database_id>][;encrypt=false]
A SQL server URL contains the following information:
jdbc— The protocol is alwaysjdbc.sqlserver— The server type is alwayssqlserver.<server_name>— The name or IP address of the host where the source server is running.<port>— The port number that the source database listener is monitoring.<database_id>— The name of the source database.
Ensure these values are set in the toolkit.properties file:
SRC_DB_USER— Specifies the name of a privileged SQL Server user.SRC_DB_PASSWORD— Contains the password of the specified user. Provide the password without any surrounding quotes.
JTDS URL
jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://<server_name>:<port>/<database_id>
Tip
The JTDS driver is an open source JDBC 3.0 type 4 driver that supports older versions of Microsoft SQL Server. See http://jtds.sourceforge.net/. When connecting newer versions of Microsoft SQL Server with Migration Toolkit, the Microsoft JDBC Driver for SQL Server is recommended.
A SQL server URL contains the following information:
jdbc— The protocol is alwaysjdbc.jtds— The driver name is alwaysjtds.sqlserver— The server type is alwayssqlserver.<server_name>— The name or IP address of the host where the source server is running.<port>— The port number that the source database listener is monitoring.<database_id>— The name of the source database.
Ensure these values are set in the toolkit.properties file:
SRC_DB_USER— Specifies the name of a privileged SQL Server user.SRC_DB_PASSWORD— Contains the password of the specified user. Provide the password without any surrounding quotes.
URL and parameters for MySQL
Migration Toolkit helps with migration from a MySQL database to an Advanced Server or PostgreSQL database. When migrating from MySQL, you must specify connection specifications for the MySQL source database in the toolkit.properties file. The connection information must include:
- The URL of the source database
- The name of a privileged user
- The password associated with the specified user
When migrating from MySQL, SRC_DB_URL takes the form of a JDBC URL. For example:
jdbc:mysql://<host_name>[:<port>]/<database_id>
The URL contains the following information:
jdbc— The protocol is alwaysjdbc.mysql— The subprotocol is alwaysmysql.<host_name>— The name or IP address of the host where the source server is running.[<port>]— The port number that the MySQL database listener is monitoring.<database_id>— The name of the source database.
Ensure these values are set in the toolkit.properties file:
SRC_DB_USER— Specifies the name of a privileged MySQL user.SRC_DB_PASSWORD— Contains the password of the specified user. Provide the password without any surrounding quotes.
Note
If datatype
tinyInt(1)is used to store byte values other than 0 and 1 in the MySQL source database, make sure to append the optional parameter?tinyInt1isBit=falsein the MySQL Connector/J JDBC Driver URL.Due to a bug in the MySQL Connector/J JDBC Driver 8.0.26, the migration of foreign key constraints fails in certain cases. EDB recommends that you don't use this driver for migrating data using Migration Toolkit. Instead, use MySQL Connector/J JDBC Driver 8.0.30 or later.
For detailed information about this bug, see the MySQL bug report.
TINYINT(1) is mapped to BIT(1) in PostgreSQL/EDB Postgres Advanced Server (which might not be expected in some cases). But as the MySQL JDBC driver reports it as BIT(1), Migration Toolkit maps it to BIT(1) in PostgreSQL/EDB Postgres Advanced Server.
Unlike TINYINT(1) that can hold the values -128 to 127, BIT(1) can hold only 0 and 1. So if you're storing any value other than 0 and 1 in this field, you might need to change the default behavior of the MySQL JDBC driver so that the driver reports it as TINYINT.
To change this behavior, set the following URL option in the connection string:
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/world?tinyInt1isBit=false
In this case, the JDBC driver reports TINYINT(1) as TINYINT and is mapped to SMALLINT in the target PostgreSQL/EDB Postgres Advanced Server.
URL and parameters for Sybase
Migration Toolkit helps with migration from a Sybase database to an Advanced Server database. When migrating from Sybase, you must specify connection specifications for the Sybase source database in the toolkit.properties file. The connection information must include:
- The URL of the source database
- The name of a privileged user
- The password associated with the specified user
When migrating from Sybase, SRC_DB_URL takes the form of a JTDS URL. For example:
jdbc:jtds:sybase://<host_name>[:<port>]/<database_id>
Tip
For an open source JDBC 3.0 type 4 driver for Sybase ASE and older versions of Microsoft SQL Server, see http://jtds.sourceforge.net/.
A Sybase URL contains the following information:
jdbc— The protocol is alwaysjdbc.jtds— The driver name is alwaysjtds.sybase— The server type is alwayssybase.<host_name>— The name or IP address of the host where the source server is running.<port>— The port number that the Sybase database listener is monitoring.<database_id>— The name of the source database.
Ensure these values are set in the toolkit.properties file:
SRC_DB_USER— Specifies the name of a privileged Sybase user.SRC_DB_PASSWORD— Contains the password of the specified user. Provide the password without any surrounding quotes.